In addition to two types of stroke—ischemic, which accounts for about three-quarters of strokes, and hemorrhagic—many people are also diagnosed as having "mini strokes." These three terms are described below:
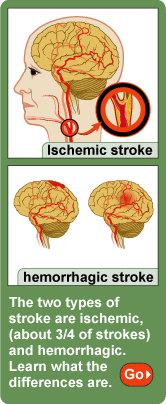
- Ischemic stroke: Results from a blockage or narrowing of a blood vessel due to plaque build-up or a blood clot. The carotid artery (the main vessel carrying blood to the brain) is most commonly affected.
- Hemorrhagic stroke:
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage occurs when an aneurysm (a weak spot in a blood vessel that fills with blood) bursts, causing bleeding on the outer edge of the brain.
- Intracerebral hemorrhage, which happens deep in the brain, results when blood leaks from a tear in a blood vessel.
- "Mini strokes" (TIAs): People who have "mini-strokes" (also called transient ischemic attacks or TIAs) are at greatly increased risk for suffering a major stroke. Treatment with blood thinners, such as aspirin or heparin, may reduce this risk.
Warning Signs of Stroke
Any of the following symptoms could indicate a stroke, which demands immediate medical attention:
- Sudden numbness, weakness or paralysis in the face, arm, or leg (often on one side of the body)
- Sudden difficulty talking or understanding speech
- Sudden confusion
- Vision disturbances
- Dizziness
- Severe, unexplained headaches
Source: National Stroke Association

No comments:
Post a Comment